因其“发展了对溶液中生物分子获取高分辨率结构的冷冻电子显微术”,瑞典皇家科学院授予了 Jacques Dubochet,Joachim Frank 以及 Richard Henderson 2017 年度诺贝尔化学奖。2017 诺贝尔化学奖科学背景:冷冻电子显微术的发展
Gatan 的直接探测相机 (K3® 与 K2®) 背后的技术与创新,引领了冷冻电子显微术的进展。
什么是单颗粒冷冻电子显微术 (SINGLE-PARTICLE CRYO-EM)?
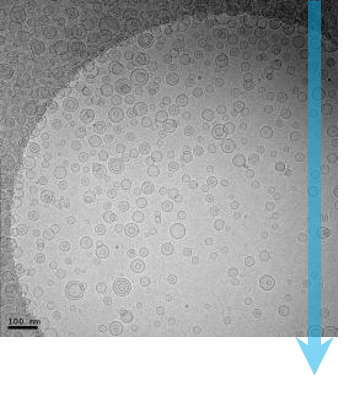
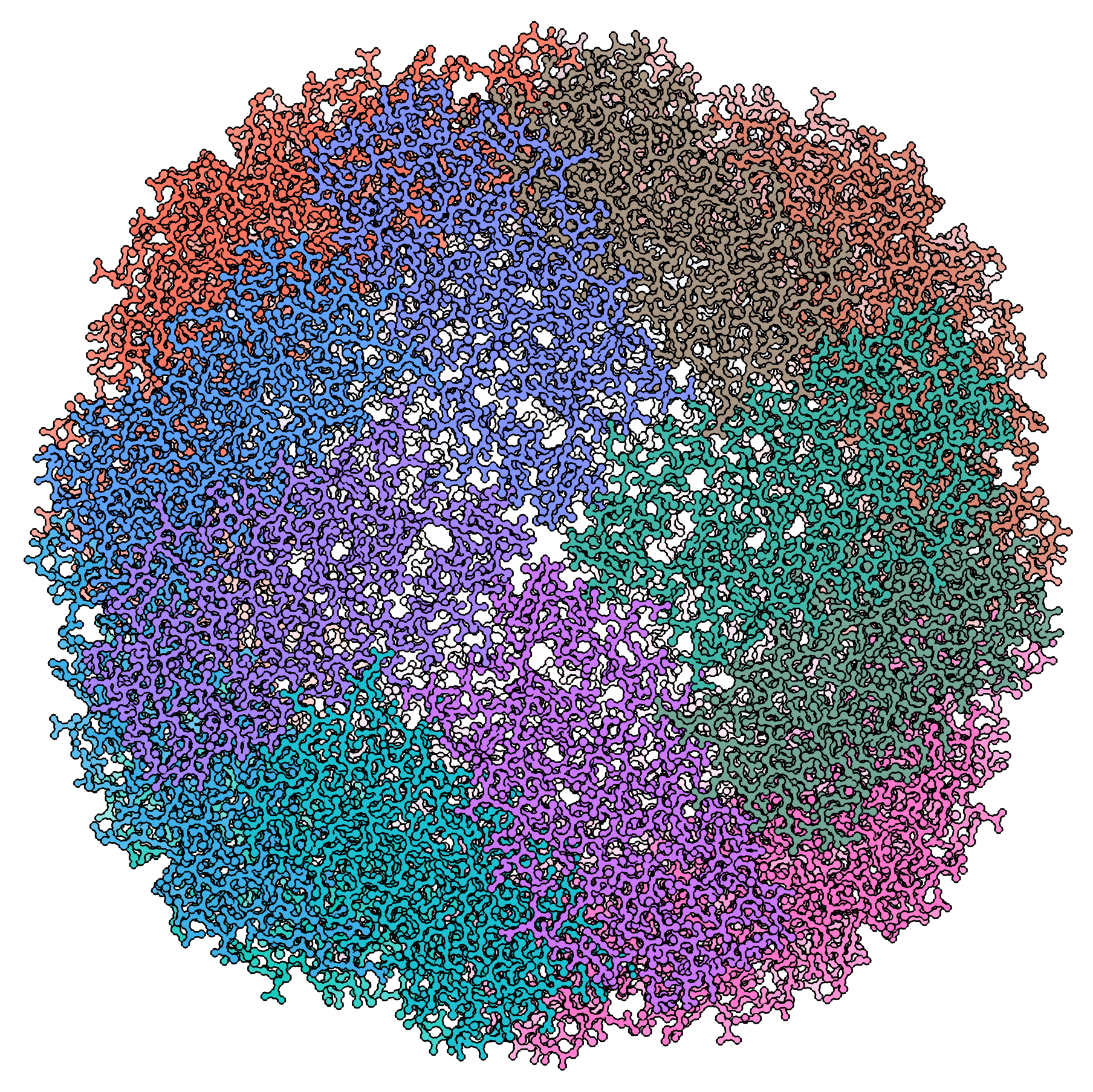 单颗粒冷冻电子显微术 (cryo-EM) 是一项逐步普及的技术,结构生物学家利用这项技术以原子级的分辨率进行结构解析。这项技术实现了对 X 射线晶体学的补充,因为它无需使用晶体样品即可显示结构细节。通过在玻璃态(非晶)冰中观察冷冻含水样品,可以保留天然状态的样品超微结构、缓冲液成分和配位体分布。冷冻电子显微术同时也是对核磁共振 (NMR) 结构研究的补充,因为它可研究大于 90 kDa 的样品。结构生物学家频繁使用冷冻电子显微术来研究病毒、小细胞器和生物大分子复合物,纯化蛋白以及超分子组装体或机器中的分子间相互作用。
单颗粒冷冻电子显微术 (cryo-EM) 是一项逐步普及的技术,结构生物学家利用这项技术以原子级的分辨率进行结构解析。这项技术实现了对 X 射线晶体学的补充,因为它无需使用晶体样品即可显示结构细节。通过在玻璃态(非晶)冰中观察冷冻含水样品,可以保留天然状态的样品超微结构、缓冲液成分和配位体分布。冷冻电子显微术同时也是对核磁共振 (NMR) 结构研究的补充,因为它可研究大于 90 kDa 的样品。结构生物学家频繁使用冷冻电子显微术来研究病毒、小细胞器和生物大分子复合物,纯化蛋白以及超分子组装体或机器中的分子间相互作用。
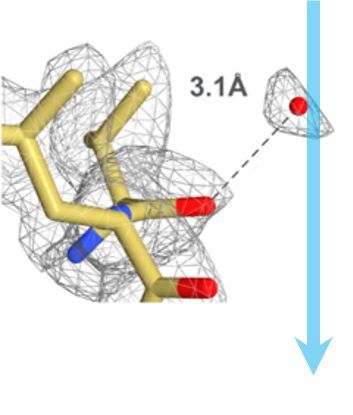
在单颗粒冷冻电子显微术中,通过透射电子显微镜 (TEM) 记录每种样品的数千乃至数十万个相同但取向随机分布的微粒(分子)的高分辨率图像。然后使用图像分类算法对这些图像进行分组、对齐和平均,以区分三维分子的不同取向。对于优质样品,冷冻电子显微术能够以优于 1.5 Å的分辨率 解析分子结构;而仅仅几年之前,这样的分辨率水平还是令人不敢想象的。
冷冻电子显微术分辨率的迅速提升被称为“分辨率革命”,它是直接探测相机带来的直接结果。传统的电子显微术相机通过闪烁体将电子图像转换为光图像,并通过光纤面板将图像传输到 CCD 或 CMOS 图像传感器,并以模拟信号方式进行记录。结果经过这样的转换和记录后,会导致高分辨率细节丢失,这使得冷冻电子显微术一直无法发挥它的真正潜力。
如今,直接探测相机可以直接对电子图像进行观测,从而避免了传统相机信号转换步骤所造成的细节丢失。Gatan K3 相机是一款独具特色的直接探测相机,采用了超分辨率电子计数技术来记录图像。这项技术可以对单个的成像电子进行实时侦测和计数,同时排除模拟读出的噪声。正如 Gatan 的直接探测相机所示在 0.5 Nyquist 上的量子探测效率 (DQE)的优异表现。
分辨率的有效界限
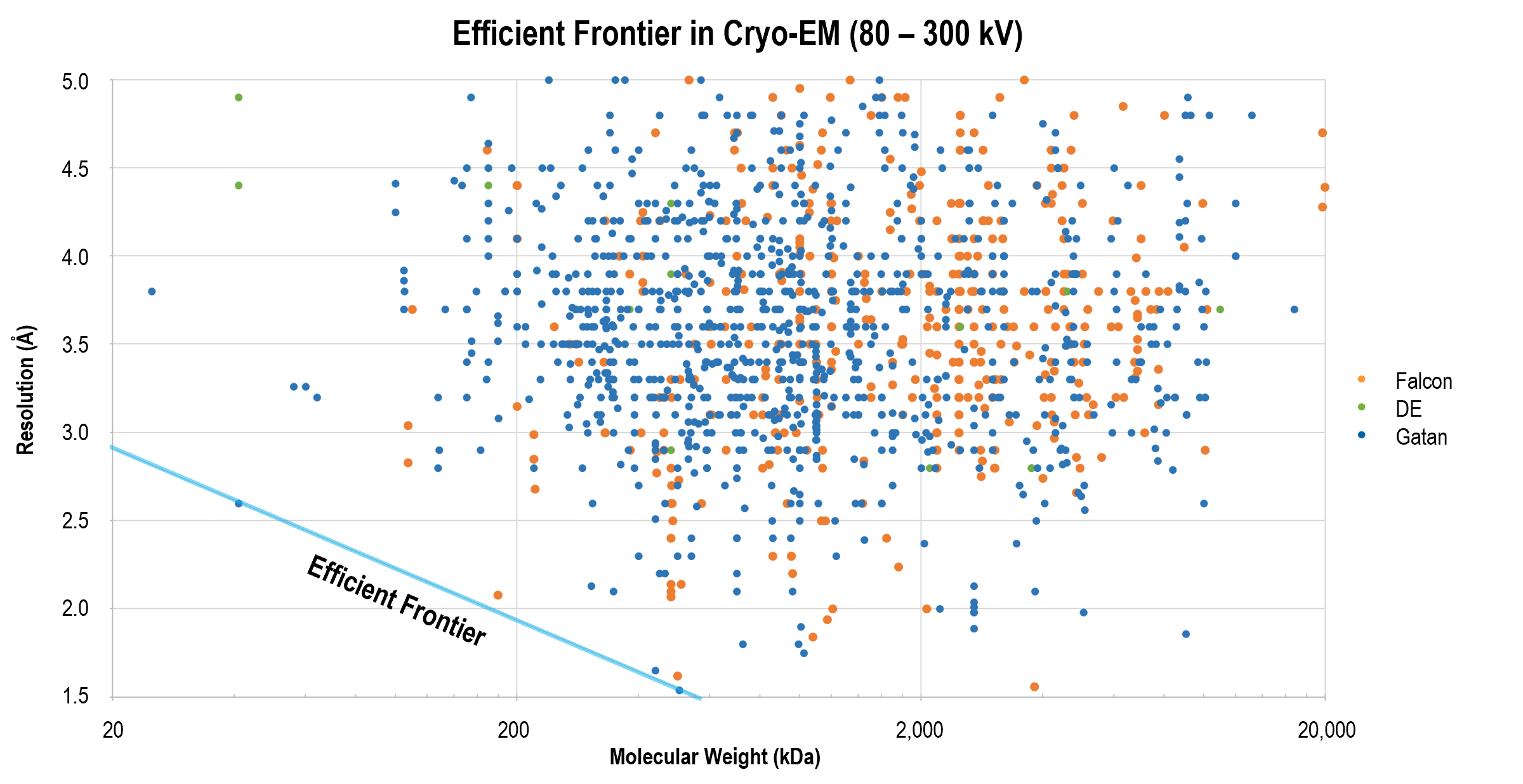
Gatan 的直接探测相机,通常与 GIF Quantum LS 成像过滤系统结合使用,不断取得了刷新分辨率有效界限的突破性成果。许多前沿结果的发表,展示了运用这些产品,以及更优的数据采集和图像处理策略,对更小分子获取更高分辨率重构,例如β-半乳糖苷酶的 2.2 Å 结构。
上图显示了业已发表的单颗粒冷冻电子显微术获得的结构的翻遍率和分子量比较。在跨越了广泛分子量区间的分辨率前沿的结构中运用了 Gatan 的直接探测相机。
单颗粒冷冻电子显微术的优势
既然单颗粒冷冻电子显微术能够提供媲美 X 射线晶体学的结构分辨率,同时该技术具有许多独特的优势,增加了其对结构生物学家的吸引力:
| 功能 | 优势 |
|---|---|
| 在天然含水状态下检测结构 | 在生物相关环境中保存样品,包括样本浓度和缓冲液组分 |
| 支持研究较大的组装体 | 可用于表征大于 150 kDa 且包含多种亚单元,抑或非均质的或者极难结晶的分子 |
| 揭示原子级分辨率的结构 | 除了 α 螺旋和 β 褶板,还可观察不对称的侧链、氢键和水分子 |
| 控制化学环境 | 您可改变实验条件,以检测分子在不同功能状态下的行为 |
| 消除结晶步骤 | 避免耗时较长且不确定的制备步骤;缩短您的发表时间 |
Workflow for single-particle cryo-EM
|
|
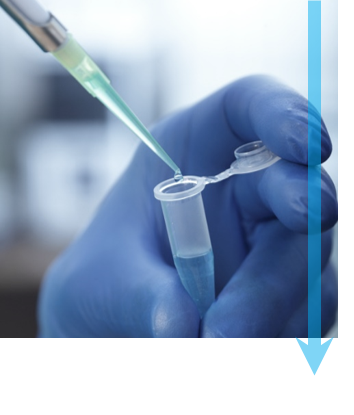
第 1 步:提纯 要使用单一微粒冷冻电子显微术研究分子,样品必须经过提纯并且结构必须完整,才能实现优质的 3D 重建。理想情况下,您需要将样品放在缓冲液中,以保持其生化活性。样品中的分子浓度应足够高,以便您能够在显微镜下观察分子,但是不能太高而使分子聚集。最后,应优化实验条件,以使待研究的分子达到统一的构象状态。 |
|
|
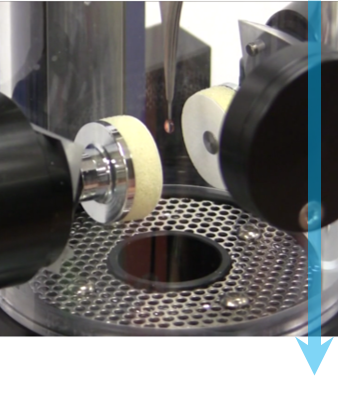
第 2 步:骤降冷冻 每个样品都将被冷冻,以防止其在显微镜的真空里冻干。近乎瞬间冷冻可以防止形成水晶体,因为水晶体会破坏样品结构。 首先,将溶液中的少量样品放到 TEM 网格上,然后使用吸水纸轻轻吸掉多余的液体。然后将 TEM 网格插入液态乙烷或乙烷/丙烷混合液,迅速润湿样品,去除热量,然后产生非晶或玻璃态冰。图中显示了吸取液体和将样品浸没在液态冷却剂中之前的 Cryoplunge® 3 系统。 |
|
|
第 3 步:转移到 TEM 中 冷冻之后,您可将样品转移到专用的 TEM 样品杆,使其保持液氮温度。为了防止样品受到污染,当您将样品装载到样品杆中时,使用冷冻工作台可以保护样品,然后从工作台转移到 TEM 的过程中,使用冷冻防护罩封住样品。如图所示的是插入到 TEM 中之前冷冻传输杆从工作台撤出的状态。 |
|
|
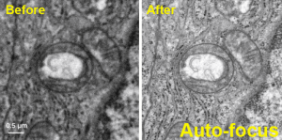
第 4 步:样品成像 当暴露在电子环境中时,样品的结构完整性会遭到破坏。在高分辨率结构信息丢失之前,通常可以使用 10–30 e-/Å2 的总剂量。为了防止样品遭到破坏,可以在捕获图像之前,使用低剂量成像步骤导航至所需的区域并将电子束聚焦。 Gatan 的直接探测相机的电子计数和超分辨率模式带来的高 DQE,可帮助您获取脆弱生物样品的优异质量图像。这些图像具有高的信噪比,可帮助您在 3D 颗粒重构过程中辨别水分子、离子和配体结构。您还可以利用 Gatan 的直接探测相机的剂量分割功能,进一步提高图像质量,该功能以最高 75 帧/秒的速度保存全幅帧,以便随后用来校正样品移动和帮助最小化漂移的影响。 |
|
|
第 5 步:分析和重构 成像之后,Gatan Microscopy Suite® 软件会帮助您进行分析,并以多种格式导出数据。Gatan 照相机获取的数据将导入各种第三方软件工具,用于进行 3D 重建和虚拟化,包括 EMAN、Frealign、Relion 及许多其他工具。图中显示了冷冻电子显微术 20S 蛋白酶体(2.8 Å 分辨率)的 3D 密度。 |
DigitalMicrograph,或称为 Gatan Microscopy Suite,驱动您的电子相机和其他附件以支持一系列重要应用,包括断层扫描、原位、谱学和衍射成像等。
-
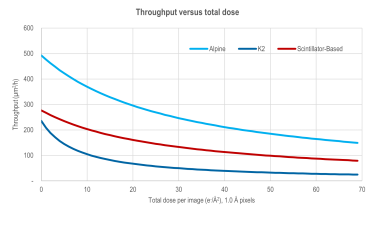 Throughput versus total dose comparison - Alpine
Throughput versus total dose comparison - Alpine
-
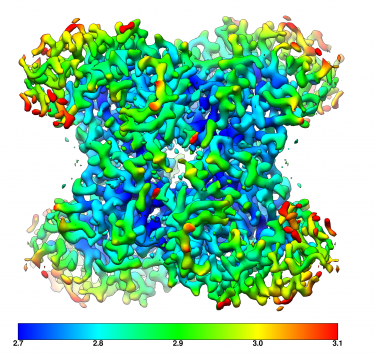 Aldolase resolved to 3.07 Å at 100 keV
Aldolase resolved to 3.07 Å at 100 keV
-
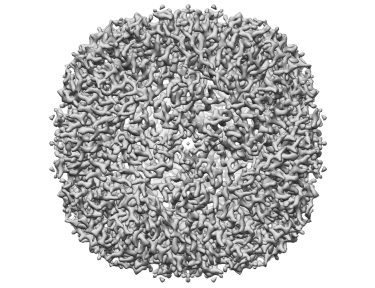 Apoferritin resolved to 2.7 Å at 100 keV
Apoferritin resolved to 2.7 Å at 100 keV
-
 Imaging molecules in their native environment: Cryo-electron tomography of PCDH15 complexes in mouse stereocilia
Imaging molecules in their native environment: Cryo-electron tomography of PCDH15 complexes in mouse stereocilia
-

 环境的重要性:Cryo-ET 揭示细胞环境对核孔复合物结构的影响
环境的重要性:Cryo-ET 揭示细胞环境对核孔复合物结构的影响
-
 Cryo EM reveals mechanisms of gating and drug modulation in 5 HT3A receptors webinar
Cryo EM reveals mechanisms of gating and drug modulation in 5 HT3A receptors webinar
-
 CryoARM/K3 组合带来的高解析分辨率:SerialEM,Latitude以及数据采集未来发展方向
CryoARM/K3 组合带来的高解析分辨率:SerialEM,Latitude以及数据采集未来发展方向
-

 结构生物学助力疫情应对
结构生物学助力疫情应对
-
 Elsa Cryo-Transfer Workstation
Elsa Cryo-Transfer Workstation
-
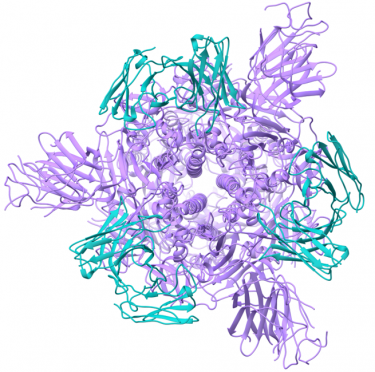 Potent neutralizing monoclonal antibodies directed to multiple epitopes on the SARS-CoV-2 spike
Potent neutralizing monoclonal antibodies directed to multiple epitopes on the SARS-CoV-2 spike
In situ structural analysis of SARS-CoV-2 spike reveals flexibility mediated by three hinges
Turoňová, B.; Sikora, M.; Schürmann, C.; Hagen, W. J. H.; Welsch, S.; Blanc, F. E. C.; von Bülow, S.; Gecht, M.; Bagola, K.; Hörner, C.; van Zandbergen, G.; Landry, J.; de Azevedo, N. T. D.; Mosalaganti, S.; Schwarz, A.; Covino, R.; Mühlebach, M. D.; Hummer, G.; Locker, J. K.; Beck, M.
Molecular architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 virus
Yao, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, N.; Xu, Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Weng, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, L,; Shi, D.; Lu, X.; Lei, J.; Crispin, M.; Shi, Y.; Li, L.; Li, S.
Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation
Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K. S.; Goldsmith, J. A.; Hsieh, C. -L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B. S.; McLellan, J. S.
Venugopal, H.; Mobbs, J.; Taveneau, C.; Fox, D. R.; Vuckovic, Z.; Knott, G.; Grinter, R.; Thal, D.; Mick, S.; Czarnik, C.; Ramm, G.
Chan, L. M.; Courteau, B. J.; Maker, A.; Wu, M.; Basanta, B.; Mehmood, H.; Bulkley, D.; Joyce, D.; Lee, B. C.; Mick, S.; Gulati, S.; Lander, G. C.; Verba, K. A.
Yang, T.; Xua, H.; Zoua, X.
Time-resolved cryo-EM using a combination of droplet microfluidics with on-demand jetting
Torino, S.; Dhurandhar, M.; Stroobants, A.; Claessens, R.; Efremov, R. G.
Szemán, A. J. K.; Stráner, P.; Jákli, I.; Hosogi, N.; Harmat, V.; Menyhárd, D. K.; Perczel, A.
Structural basis of actin filament assembly and aging
Oosterheert, W.; Klink, B. U.; Belyy, A.; Pospich, S.; Raunser, S.
Helical ultrastructure of the metalloprotease meprin α in complex with a small molecule inhibitor
Bayly-Jones, C.; Lupton, C. J.; Fritz, C.; Venugopal, H.; Ramsbeck, D.; Wermann, M.; Jäger,C.; Marco, A. D.; Schilling, S.; Schlenzig, D.; Whisstock, J. C.
Stern, A. M.; Yang, Y.; Meunier, A. L.; Liu, W.; Cai, Y.; Ericsson, M.; Liu, L.; Goedert, M.; Scheres, S. H. W.; Selkoe, D.J
Cryo-EM structure of the human NKCC1 transporter reveals mechanisms of ion coupling and specificity
Neumann, C.; Rosenbæk, L. L.; Flygaard, R. K.; Habeck, M.; Karlsen, J. L.; Wang, Y.; Larsen, K. L.; Gad, H. H.; Hartmann, R.; Lyons, J. A; Fenton, R. A.; Nissen, P.
Algal photosystem I dimer and high-resolution model of PSI-plastocyanin complex
Naschberger, A.; Mosebach, L.; Tobiasson, V.; Kuhlgert, S.; Scholz, M.; Perez-Boerema, A.; Ho, T. T. H.; Vidal-Meireles, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Hippler, M.; Amunts, A.
Chang, M. R.; Tomasovic, L.; Kuzmina, N. A.; Ronk, A. J.; Byrne, P. O.; Johnson, R.; Storm, N.; Olmedillas, E.; Hou, Y. J.; Schäfer, A.; Leist, S. R.; Tse, L. T.; Ke, H.; Coherd, C.; Nguyen, K.; Kamkaew, M.; Honko, A.; Zhu, Q.; Alter, G.; Saphire, E. O.; McLellan, J. S.; Griffiths, A.; Baric, R. S.; Bukreyev. A.; Marasco. W. A.
Frieg, B.; Geraets, J. A.; Strohäker, T.; Dienemann, C.; Mavroeidi, P.; Jung, B. C.; Kim, W. S.; Lee, S. J.; Xilouri, M.; Zweckstetter. M.; Schröder. G. F.
Lyu, M.; Ayala, J. C.; Chirakos, I.; Su, C. -C.; Shafer, W. M.; Yu, E. W.
Organic crystal growth: Hierarchical self-assembly involving nonclassical and classical steps
Biran, I.; Rosenne, S.; Weissman, H.; Tsarfati, Y.; Houben, L.; Rybtchinski. B.
Structure of the PAPP-ABP5 complex reveals mechanism of substrate recognition
Judge, R. A.; Sridar, J.; Tunyasunvunakool, K.; Jain, R.; Wang, J. C. K.; Ouch, C.; Xu, J.; Mafi, A.; Nile, A. H.; Remarcik, C.; Smith, C. L.; Ghosh, C.; Xu, C.; Stoll, V.; Jumper, J.; Singh, A. H.; Eaton, D.; Hao, Q.
Structures of a phycobilisome in light-harvesting and photoprotected states
Domínguez-Martín, M. A.; Sauer, P. V.; Kirst, H.; Sutter, M.; Bína, D.; Greber, B. J.; Nogales, E. ;Polívka, T.; Kerfeld, C. A.
Zhu, J.; Huang, W.; Zhao, J., Huynh, L.; Taylor, D. J.; Harris, M. E.
Kuhle, B.; Hirschi, M.; Doerfel, L. K.; Lander, G. C.; Schimmel, P.
Miyakawa, T.; Yang, J.; Kawasaki, M.; Adachi, N.; Fujii, A.; Miyauchi, Y.; Muramatsu, T.; Moriya, T.; Senda, T.; Tanokura, M.
Zhao, J.; Makhija, S.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Muralidharan, M.; Huang, B.; Cheng, Y.
Mechanistic details of CRISPR-associated transposon recruitment and integration revealed by cryo-EM
Park, J. U.; Tsai, A. W. -T.; Chen, T. H.; Peters, J. E.; Kellogg, E. H.
Specific recognition and ubiquitination of slow-moving ribosomes by human CCR4-NOT
Absmeier, E.; Chandrasekaran, V.; O'Reilly, F. J.; Stowell, J. A. W.; Rappsilber, J.; Passmore, L. A.
Peck, J. V.; Strauss, J. D.; Fay, J. F.
Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles
Cai, K.; Sibert, B. S.; Kumar, A.; Yang, J.; Larson, M.; Thompson, K.; Wright, E. R.
Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Chiu, W.; Cui, Y.
Cryo-EM structure of an active bacterial TIR–STING filament complex
Morehouse, B. R.; Yip, M. C. J.; Keszei, A. F. A.; McNamara-Bordewick, N. K.; Shao, S.; Kranzusch, P. J.
Maintaining the momentum in cryoEM for biological discovery
Thompson, R.; Halfon, Y.; Aspinall, L.; White, J.; Hirst, I. J.; Wang, Y.; Darrow, M.; Muench, S. P.
Structural analysis of the basal state of the Artemis:DNA-PKcs complex
Watanabe, G.; Lieber, M. R.; Williams, D. R.
Flipped over U: structural basis for dsRNA cleavage by the SARS-CoV-2 endoribonuclease
Frazier, M. N.; Wilson, I. M.; Krahn, J. M.; Butay, K. J.; Dillard, L. B.; Borgnia, M. J.; Stanley, R. E.
Structures and gating mechanisms of human bestrophin anion channels
Owji, A. P.; Wang, J.; Kittredge, A.; Clark, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hendrickson, W. A.; Yang, T.
Structural insights into dsRNA processing by Drosophila Dicer-2–Loqs-PD
Su, S.; Wang, J.; Deng, T.; Yuan, X.; He, J.; Liu, N.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H. -W.; Ma, J.
Structures and mechanism of the plant PIN-FORMED auxin transporter
Ung, K. L.; Winkler, M.; Schulz, L.; Kolb, M.; Janacek, D. P.; Dedic, E.; Stokes, D. L.; Hammes, U. Z.; Pedersen, B. P.
Structure and flexibility of the yeast NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex
Zukin, S. A.; Marunde, M. R.; Popova, I. K.; Nogales, E.; Patel, A. B.
Role of aIF5B in archaeal translation initiation
Kazan, R.; Bourgeois, G.; Lazennec-Schurdevin, C.; Larquet, E.; Mechulam, Y.; Coureux, P. -D.; Schmitt, E.
Ion complexation waves emerge at the curved interfaces of layered minerals
Whittaker, M. L.; Ren, D.; Ophus, C.; Zhang, Y.; Waller, L.; Gilbert, B.; Banfield, J. F.
Compact IF2 allows initiator tRNA accommodation into the P site and gates the ribosome to elongation
Basu, R. S.; Sherman, M. B.; Gagnon, M. G.
Structural Basis for pH-gating of the K+ channel TWIK1 at the selectivity filter
Turney, T. S.; Li, V.; Brohawn, S. G.
Cryo-EM structures of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 spike
Stalls, V.; Lindenberger, J.; Gobeil, S. M. -C.; Henderson, R.; Parks, R.; Barr, M.; Deyton, M.; Martin, M.; Janowska, K.; Huang, X.; May, A.;l Speakman, M.; Beaudoin, E.; Kraft, B.; Lu, X.; Edwards, R. J.; Eaton, A.; Montefiori, D. C.; Williams, W.; Saunders, K. O.; Wiehe, K.; Haynes, B. F.; Acharya, P.
Structure of S1PR2–heterotrimeric G13 signaling complex
Chen, H.; Chen, K.; Huang, W.; Staudt, L. M.; Cyster, J. G.; Li, X.
Structure of the type V-C CRISPR-Cas effector enzyme
Kurihara, N.; Nakagawa, R.; Hirano, H.; Okazaki, S.; Tomita, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Kusakizako, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Yamashita, K.; Scott, D. A.; Nishimasu, H.; Nureki, O.
Cryogenic TEM imaging of artificial light harvesting complexes outside equilibrium
Krishnaswamy, S. R.; Gabrovski, I. A.; Patmanidis, I.; Stuart, M. C. A.; de Vries A. H.; Pshenichnikov, M. S.
Zhao, W.; Jensen, G. J.
The giant Mimivirus 1.2 Mb genome is elegantly organized into a 30 nm helical protein shield
Villalta, A.; Schmitt, A.; Estrozi, L. F.; Quemin, E. R. J.; Alempic, J. -M.; Lartigue, A.; Pražák, V.; Belmudes, L.; Vasishtan, D.; Colmant, A. M. G.; Honoré, F. A.; Couté, Y.; Grünewald, K.; Abergel, C.
Structural and functional impact by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron spike mutations
Zhang, J.; Cai, Y.; Lavine, C. L.; Peng, H.; Zhu, H.; Anand, K.; Tong, P.; Gautam, A.; Mayer, M. L.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Wang, S.; Sliz, P.; Wesemann, D. R.; Yang, W.; Seaman, M. S.; Lu, J.; Xiao, T.; Chen, B.
Capturing the swelling of solid-electrolyte interphase in lithium metal batteries
Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Oyakhire, S. T.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, Z.; Boyle, D. T.; Huang, W.; Ye, Y.; Chen, H.; Wan, J.; Bao, Z.; Chiu, W.; Cui, Y.
Nuclear pores dilate and constrict in cellulo
Zimmerli, C. E.; Allegretti, M.; Rantos, V.; Goetz, S. K.; Obarska-Kosinska, A.; Zagoriy, I.; Halavatyi, A.; Hummer, G.; Mahamid, J.; Kosinski, J.; Beck, M.
Scaffolding protein CcmM directs multiprotein phase separation in β-carboxysome biogenesis
Zang, K.; Wang, H.; Hartl, F. U.; Hayer-Hartl, M.
Alegre, K. O.; Paknejad, N.; Su, M.; Lou, J. -S.; Huang, J.; Jordan, K. D.; Eng, E. T.; Meyerson, J. R.; Hite, R. K.; Huang, X. -Y.
Emmanuel, S. N.; Smith, J. K.; Hsi, J.; Tseng, Y. -S.; Kaplan, M.; Mietzsch, M.; Chipman, P.; Asokan, A.; Robert McKenna, R.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.
Yu, H.; Hamaguchi, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Kato, K.; Kawakami, K.; Akita, F.; Yonekura, K.; Shen, J. -R.
Peng, Q.; Peng, R.; Yuan, B.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Z.; Qi, J.; Gao, G. F.; Shi, Y.
A simple pressure-assisted method for MicroED specimen preparation
Zhao, J.; Xu, H.; Lebrette, H.; Carroni, M.; Taberman, H.; Hogbom, M.; Zou, X.
Ultrapotent antibodies against diverse and highly transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants
Wang, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, E. S.; Schramm, C. A.
Wei, H.; Qian, X.; Xie, F.; Cui, D.
Native-like SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein expressed by ChAdOx1 nCoV-19/AZD1222 vaccine
Watanabe, Y.; Mendonça, L.; Allen, E. R.; Howe, A.; Lee, M.; Allen, J. D.; Chawla, H.; Pulido, D.; Donnellan, F.; Davies, H.; Ulaszewska, M.; Belij-Rammerstorfer, S.; Morris, S.; Krebs, A. -S.; Dejnirattisai, W.; Mongkolsapaya, J.; Supasa, P.; Screaton, G. R.; Green, C. M.; Lambe, T.; Zhang, P.; Gilbert, S. C.; Crispin, M.
Simplified approach for preparing graphene oxide TEM grids for stained and vitrified biomolecules
Kumar, A.; Sengupta, N.; Dutta, S.
Shafiq, A.; Suwakulsiri, W.; Rai, A.; Chen, M.; Greening, D. W.; Zhu, H. -J.; Xu, R.; Simpson, R. J.
Structure of a microtubule-bound axonemal dynein
Walton, T.; Wu, H.; Brown, A.
Mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 polymerase stalling by remdesivir
Kokic, G.; Hillen, H. S.; Tegunov, D.; Dienemann, C.; Seitz, F.; Schmitzova, J.; Farnung, L.; Siewert, A.; Höbartner, C.; Cramer, P.
Structure-guided multivalent nanobodies block SARS-CoV-2 infection and suppress mutational escape
Koenig, P. -D.; Das, H.; Liu H.; Kümmerer, B. M.; Gohr, F. N.; Jenster, L. -M.; Schiffelers, L. D. J.; Tesfamariam, Y. M.; Uchima, M.; Wuerth, J. D.; Gatterdam, K.; Ruetalo, N.; Christensen, M. H.; Fandrey, C. I.; Normann, S.; Tödtmann, J.; M. P.; Pritzl, S.; Hanke, L.; Boos, J.; Yuan, M.; Zhu, X.; Schmid-Burgk, J. L.; Kato, H.; Schindler, M.; Wilson, I. A.; Geyer, M.; Ludwig, K. U.; Hällberg, M.; Wu, N. C.; Schmidt, F. I.
Stabilizing the closed SARS-CoV-2 spike trimer
Juraszek, J.; Rutten, L.; Blokland, S.; Bouchier, P.; Voorzaat, R.; Ritschel, T.; Bakkers, M. J. G.; Renault , L. L. R.; Langedijk, J. P. M.
Development and structural basis of a two-MAb cocktail for treating SARS-CoV-2 infections
Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Gu, C.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, W.; Hong, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, C.; Hong, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Qiao, W.; Zang, J.; Kong, L.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Qu, D.; Lavillette, D.; Tang, H.; Deng, Q.; Xie, Y.; Cong, Y.; Huang, Z.
Yan, L.; Ge, J.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, S.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guddat, L. W.; Wang, Q.; Rao, Z.; Lou, Z.
Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Han, W.; Hong, X.; Wang, Y.; Hong, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, K.; Zheng, W.; Kong, L.; Wang, F.; Zuo, Q.; Huang, Z.; Cong, Y.
They spent 12 years solving a puzzle. It yielded the first COVID-19 vaccines.
Kramer, J.
Mihelc. E. M.; Baker, S. C.; Lanman, J. K.
Yuan, S.; Peng, L.; Park, J. J.; Hu, Y.; Devarkar, S. C.; Dong, M. B.; Shen, Q.; Wu, S.; Chen, S.; Lomakin, I. B.; Xiong, Y.
Zhou, T.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Gorman, J.; Rapp, M.; Cerutti, G.; Chuang, G. -Y.; Katsamba, P. S.; Sampson, J. M.; Schön, A.; Bimela, J.; Boyington, J. C.; Nazzari, A.; Olia, A. S.; Shi, W.; Sastry, M.; Stephens, T.; Stuckey, J.; Teng, I. -T.; Kwong, P. D
De novo design of potent and resilient hACE2 decoys to neutralize SARS-CoV-2
Linsky, T. W.; Vergara, R.; Codina, N.; Nelson, J. W.; Walker, M. J.; Su, W.; Barnes, C. O.; Hsiang, T. -Y.; Esser-Nobis, K.; Yu, K.; Reneer, B.; Hou, Y. J.; Priya, T.; Mitsumoto, M.; Pong, A.; Lau, Y.; Mason, M. L.; Chen, J.; Chen, A.; Berrocal, T.; Peng, H.; Clairmont, N. S.; Castellanos, J.; Lin, Y. -R..; Josephson-Day, A.; Baric, R. S.; Fuller, D. H.; Walkey, C. D.; Ross, T. M.; Swanson, R.; Bjorkman, P. J.; Gale Jr., M.; Blancas-Mejia, L. M.; Yen, H. -L.; Silva, D. -A.
Yao, H.; Sun, Y.; Deng, Y. -Q.; Wang, N.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, N. -N.; Li, X. -F.; Kong, C.; Xu, Y. -P.; Chen, Q.; Cao, T. -S.; Zhao, H.; Yan, X.; Cao, L.; Lv, Z.; Zhu, D.; Feng, R.; Wu, N.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, R. -R.; Lv, Q.; Sun, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, R.; Yang, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Cheng, L.; Qiu, H.; Huang, X. -Y.; Weng, T.; Shi, D.; Jiang, W.; Shao, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, T.; Lang, G.; Qin, C. -F.; Li, L.; Wang, X.
Structure-based development of human antibody cocktails against SARS-CoV-2
Wang, N.; Sun, Y.; Feng, R.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Deng, Y. -Q.; Wang, L.; Cui, Z.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y. -J.; Li, W.; Zhu, F. -C.; Qin, C. -F.; Wang, X.
Structural analysis of full-length SARS-CoV-2 spike protein from an advanced vaccine candidate
Bangaru, S.; Ozorowski, G.; Turner, H. L.; Antanasijevic, A.; Huang, D.; Wang, X.; Torres, J. L.; Diedrich, J. K.; Tian, J. -H.; Portnoff, A. D.; Patel, N.; Massare, M. J.; Yates III, J. R.; Nemazee, D.; Paulson, J. C.; Glenn, G.; Smith, G.; Ward, A. B.
Ultrapotent human antibodies protect against SARS-CoV-2 challenge via multiple mechanisms
Tortorici, M. A.; Beltramello, M.; Lempp, F. A.; Pinto, D.; Dang, H. V.; Rosen, L. E.; McCallum, M.; Bowen, J.; Minola, A.; Jaconi, S.; Zatta, F.; De Marco, A.; Guarino, B.; Bianchi, S.; Lauron, E. J.; Tucker, H.; Zhou, J.; Peter, A.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; Wojcechowskyj, J. A.; Case, J. B.; Chen, R. E.; Kaiser, H.; Montiel-Ruiz, M.; Meury, M.; Czudnochowski, N.; Spreafico, R.; Dillen, J.; Ng, C.; Sprugasci, N.; Culap, K.; Benigni, F.; Abdelnabi, R.; Foo, S. -Y. C.; Schmid, M. A.; Cameroni, E.; Riva, A.; Gabrieli, A.; Galli, M.; Pizzuto. M. S.; Neyts, J.; Diamond, M. S.; Virgin, H. W.; Snell, G.; Corti, D.; Fink, K.; Veesler, D.;
SARS-CoV-2 structure and replication characterized by in situ cryo-electron tomography
Klein, S.; Cortese, M.; Winter, S. L.; Wachsmuth-Melm, M.; Neufeldt, C. J.; Cerikan, B.; Stanifer, M. L.; Boulant, S.; Bartenschlager, R.; Chlanda , P.
Architecture of a SARS-CoV-2 mini replication and transcription complex
Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, J.; Zheng, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, T.; Jia, Z.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Ra, Z.; Lou, Z.
Piccoli, L.; Park, Y. -J.; Tortorici, M. A.; Czudnochowski, N.; Walls, A. C.; Beltramello, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Pinto, D.; Rosen, L. E.; Bowen, J. E.; Acton, O. J.; Jaconi, S.; Guarino, B.; Minola, A.; Zatta, F.; Sprugasci, N.; Bassi, J.; Peter, A.; De Marco, A.; Nix, J. C.; Mele, F.; Jovic, S.; Rodriguez, B. F.; Gupta, S. V.; Jin, F.; Piumatti, G.; Presti, G. L.; Pellanda, A. F.; Biggiogero, M.; Tarkowski, M.; Pizzuto, M. S.; Cameroni, E.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; Smithey, M.; Hong, D.; Lepori, V.; Albanese, E.; Ceschi, A.; Bernasconi, E.; Elzi, L.; Ferrari, P.; Garzoni, C.; Riva, A.; Snell, G.; Sallusto, F.; Fink, K.; Virgin, H. W.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Corti, D.; Veesler, D.
Du, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yu, P.; Qi, F.; Wang, G.; Du, X.; Bao, L.; Deng, W.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Nie, J.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, H.; Liu, R.; Gong, S.; Xu, H.; Yisimayi, A.; Qin, C.
Guo, L.; Bi, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cai, X.; Jiang, S.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, L.; Dang, B.
Free fatty acid binding pocket in the locked structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
Toelzer, C.; Gupta, K.; Yadav, S. K. N.: Borucu, U.; Davidson, A. D.; Williamson, M. K.; Shoemark, D. K.; Garzoni, F.; Staufer, O.; Milligan, R.; Capin, J.; Mulholland, A. J.; Spatz, J.; Fitzgerald, D.; Berger, I.; Schaffitzel, C.
An ultrapotent synthetic nanobody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 by stabilizing inactive spike
Schoof, M.; Faust, B.; Saunders, R. A.; Sangwan, S.; Rezelj, V.; Hoppe, N.; Boone, M.; Billesbølle, C. B.; Puchades, C.; Azumaya, C. M.; Kratochvil, H. T.; Zimanyi, M.; Deshpande, I.; Liang, J.; Dickinson, S.; Nguyen, H. C.; Chio, C. M.; Merz, G. E.; Thompson, M. C.; Diwanji, D.; Schaefer, K.; Anand, A. A.; Dobzinski, N.; Zha, B. S.; Simoneau, C. R.; Leon, K.; White, K. M.; Chio, U. S.; Gupta, M.; Jin, M.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Bulkley, D.; Sun, M.; Smith, A. M.; Rizo, A. N.; Moss, F.; Brilot, A. F.; Pourmal, S.; Trenker, R.; Pospiech, T.; Gupta, S.; Barsi-Rhyne, B.; Belyy, V.; Barile-Hill, A. W.; Nock, S.; Liu, Y.; Krogan, N. J.; Ralston, C. Y.; Swaney, D. L.; García-Sastre, A.; Ott, M.; Vignuzzi, M.; QCRG Structural Biology Consortium; Walter, P.; Manglik, A.
Custódio, T. F.; Das, H.; Sheward, D. J.; Hanke, L.; Pazicky, S.; Pieprzyk, J.; Sorgenfrei, M.; Schroer, M. A.; Gruzinov, A. Y.; Jeffries, C. M.; Graewert, M. A.; Svergun, D. I.; Dobrev, N.; Remans, K.; Seeger, M. A.; McInerney, G. M.; Murrell, B.; Hällberg, B. M.; Löw, C.
The architecture of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 with postfusion spikes revealed by cryo-EM and cryo-ET
Liu, C.; Mendonça, L.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shen, C.; Liu, J.; Ni, T.; Ju, B.; Liu, C.; Tang, X.; Wei, J.; Ma, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Zhang, P.
Zhou, T.; Teng, I. -T.; Olia, A. S.; Cerutti, G.; Gorman, J.; Nazzari, A.; Shi, W.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Katsamba, P. S.; Petrova, Y.; Banach, B. B.; Fahad, A. S.; Liu, L.; Lopez Acevedo, S. N.; Madan, B.; de Souza, M. O.; Pan, X.; Wang, P.; Wolfe, J. R.; Yin, M.; Ho, D. D.; Phung, E.; DiPiazza, A.; Chang, L. A.; Abiona, O. M.; Corbett, K. S.; DeKosky, B. J.; Graham, B. S.; Mascola, J. R.; Misasi, J.; Ruckwardt, T.; Sullivan, N. J.; Shapiro, L.; Kwong, P. D.
De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors
Cao, L.; Goreshnik, I.; Coventry, B.; Case, J. B.; Miller, L.; Kozodoy, L.; Chen, R. R.; Carter, L.; Walls, A. C.; Park, Y. -J.; Strauch, E. -M.; Stewart, L.; Diamond, M. S.; Veesler, D.; Baker, D.
SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody structures inform therapeutic strategies
Barnes, C. O.; Jette, C. A.; Abernathy, M. E.; Dam, K. -M., A.; Esswein, S. R.; Gristick, H. B.; Malyutin, A. G.; Sharaf, N. G.; Huey-Tubman, K. E.; Lee, Y. E.; Robbiani, D. F.; Nussenzweig, M. C.; West Jr., A. P.; Bjorkman, P. J.
Broad host range of SARS-CoV-2 and the molecular basis for SARS-CoV-2 binding to cat ACE2
Wu, L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Han, P.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Meng, Y.; Pan, X.; Qiao, C.; Tian, S.; Du, P.; Song, H.; Shi, W.; Qi, J.; Wang, H. -W.; Yan, J.; Gao, G. F.; Wang, Q.
Structure-based design of prefusion-stabilized SARS-CoV-2 spikes
Hseih, C. -L.; Goldsmith, J. A.; Schaub, J. M.; Divenere, A. M.; Kuo, H. -C.; Javanmardi, K.; Le, K. C.; Wrapp, D.; Lee, A. G.; Liu, Y.; Chou, C. -W.; Byrne, P. O.; Hjorth, C. K.; Johnson, N. V.; Ludes-Meyers, J.; Nguyen, A. W.; Park, J.; Wang, N.; Amengor, D.; Lavinder, J. J.; Ippolito, G. C.; Maynard, J. A.; Finkelstein, I. J.; McLellan, J. S.
Structural basis for neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV by a potent therapeutic antibody
Lv, Z.; Deng, Y. -Q.; Ye, Q.; Cao, L.; Sun, C. -Y.; Fan, C.; Huang, W.; Sun, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, N.; Nie, J.; Cui, Z.; Zhu, D.; Shaw, N.; Li, X. -F.; Li, Q.; Xie, L.; Wang, Y.; Rao, Z.; Qin, C. -F.; Wang, X.
Chen, J.; Malone, B.; Llewellyn, E.; Grasso, M.; Shelton, P. M. M.; Olinares, P. D. B.; Maruthi, K.; Eng, E. T.; Vatandaslar, H.; Chait, B. T.; Kapoor, T. M.; Darst, S. A.; Campbell, E. A.
Receptor binding and priming of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 for membrane fusion
Benton, D. J.; Wrobel, A. G.; Xu, P.; Roustan, C.; Martin, S. R.; Rosenthal, P. B.; Skehel, J. J.; Gamblin, S. J.
SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 binds the ribosomal mRMA channel to inhibit translation
Schubert, K.; Karousis, E. D.; Jomaa, A.; Scaiola, A.; Echeverria, B.; Gurzeler, L. -A.; Leibundgut, M.; Thiel, V.; Mühlemann, O.; Ban, N.
Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by destruction of the prefusion spike
Huo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhou, D.; Duyvesteyn, H. M. E.; Ginn, H. M.; Carrique, L.; Malinauskas, T.; Ruza, R. R.; Shah, P. N. M.; Tan, T. K.; Rijal, P.; Coombes, N.; Bewley, K. R.; Tree, J. A.; Radecke, J.; Paterson, N. G.; Supasa, P.; Mongkolsapaya, J.; Screaton, G. R.; Carroll, M.; Townsend, A.; Fry, E. E.; Owens, R. J.; Stuart, D. I.
An alpaca nanobody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 by blocking receptor interaction
Hanke, L.; Perez, L. V.; Sheward, D. J.; Das, H.; Schulte, T.; Moliner-Morro, A.; Corcoran, M.; Achour, A.; Hedestam, G. B.; Hällberg, B. M.; Murrell, B.; McInerney, G. M.
Structural basis for translational shutdown and immune evasion by the Nsp1 protein of SARS-CoV-2
Thoms, M.; Buschauer, R.; Ameismeier, M.; Loepke, L.; Denk, T.; Hirschenberger, M.; Kratzat, H.; Hayn, M.; Mackens-Kiani, T.; Cheng, J.; Straub, J. H.; Sturzel, C. M.; Frohlich, T.; Berninghausen, O.; Becker, T.; Kirchhoff, F.; Sparrer, K. M.; Beckmann, R.
Studies in humanized mice and convalescent humans yield a SARS-CoV-2 antibody cocktail
Hansen, J.; Baum, A.; Pascal, K. E.; Russo, V.; Giordano, S.; Wloga, E.; Fulton, B. O.; Yan, Y.; Koon, K.; Patel, K.; Chung, K. M.; ermann, A.; Ullman, E.; Cruz, J.; Rafique, A.; Huang, T.; Fairhurst, J.; Libertiny, C.; Malbec, M.; Lee, W. -Y.; Welsh, R.; Farr, G.; Pennington, S.; Deshpande, D.; Cheng, J.; Watty, A.; Bouffard, P.; Babb, R.; Levenkova, N.; Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Hernandez, A. R.; Saotome, K.; Zhou, Y.; Franklin, M.; Sivapalasingam, S.; Lye, D. C.; Weston, S.; Lopgue, J.; Haupt, R.; Frieman, M.; Chen., G.; Olson, W.; Murphy, A. J.; Stahl, N.; Yancopoulos, G. D.; Kyratsous, C. A.
Barnes, C. O.; West Jr., A. P.; Huey-Tubman, K. E.; Hoffmann, M. A. G.; Sharaf, N. G.; Hoffman, P. R.; Koranda, N.; Gristick, H. B.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F.; Lorenzi, J. C. C.; Finkin, S.; Hägglöf, T.; Hurley, A.; Millard, K. G.; Weisblum, Y.; Schmidt, F.; Hatziioannou, T.; Bieniasz, P. D.; Caskey, M.; Robbiani, D. F.; Nussenzweig, M. C.; Bjorkman. P. J.
A neutralizing human antibody binds to the N-terminal domain of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2
Chi, X.; Yan, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, P.; Dong, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Song, X.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, L.; Fu, L.; Hou, L.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, W.
Structural basis for the neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by an antibody from a convalescent patient
Zhou, D.; Duyvesteyn, H. M. E.; Chen, C. -P.; Huang, C. -G.; Chen, T. -H.; Shih, S. -R.; Lin, Y. -C.; Cheng, C. -Y.; Cheng, S. -H.; Huang, Y. -C.; Lin, T. -Y.; Ma, C.; Huo, J.; Carrique, L.; Malinauskas, T.; Ruza, R. R.; Shah, P. N. M.; Tan, T. K.; Rijal, P.; Donat, R. F.; Godwin, K.; Buttigieg, K. R.; Tree, J. A.; Radecke, J.; Paterson, N. G.; Supasa, P.; Mongkolsapaya, J.; Screaton, G. R.; Carroll, M. W.; Gilbert-Jaramillo, J.; Knight, M. L.; James, W.; Owens, R. J.; Naismith, J. H.; Townsend, A. R.; Fry, E. E.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, J.; Stuart, D. I.; Huang, K. -Y. A.
A thermostable, closed SARS-CoV-2 spike protein trimer
Xiong, X.; Qu, K.; Ciazynska, K. A.; Hosmillo, M.; Carter, A. P.; Ebrahimi, S.; Ke, Z.; Scheres, S. H. W.; Bergamaschi, L.; Grice, G. L.; Zhang, Y.; The CITIID-NIHR COVID-19 BioResource Collaboration; Nathan, J. A.; Baker, S.; James, L. C.; Baxendale, H. E.; Goodfellow, I.; Doffinger, R.; Briggs, J. A. G.
Structural basis for RNA replication by the SARS-CoV-2 polymerase
Wang, Q.; Wu2, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Mu, A.; Ji, W.; Yan, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Fang, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Gao, H.; Liu, F.; Ge, J.; Sun, Q.; Yang, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, Z.; Yang, H.; Lou, Z.; Jiang, B.; Guddat, L. W.; Gong, P.; Rao, Z.
Controlling the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein conformation
Henderson, R.; Edwards, R. J.; Mansouri, K.; Janowska, K.; Stalls, V.; Gobeil, S. M. C.; Kopp, M.; Li, D.; Parks, R.; Hsu, A. L.; Borgnia, M. J.; Haynes, B. F.; Acharya, P.
Cryo-EM analysis of the post-fusion structure of the SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein
Fan, X.; Cao, D.; Kong, L.; Zhang, X.
Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
Zost, S. J.; Gilchuk, P.; Case, J. B.; Binshtein, E.; Chen, R. E.; Nkolola, J. P.; Schäfer, A.; Reidy, J. X.; Trivette, A.; Nargi, R. S.; Sutton, R. E.; Suryadevara, N.; Martinez, D. R.; Williamson, L. E.; Chen, E. C.; Jones, T.; Day, S.; Myers, L.; Hassan, A. O.; Kafai, N. M.; Winkler, E. S.; Fox, J. M.; Shrihari, S.; Mueller, B. K.; Meiler, J.; Chandrashekar, A.; Mercado, N. B.; Steinhardt, J. J.; Ren, K.; Loo, Y. -M.; Kallewaard, N. L.; McCune, B. T.; Keeler, S. P.; Holtzman, M. J.; Barouch, D. H.; Gralinski, L. E.; Baric, R. S.; Thackray, L. B.; Diamond, M. S.; Carnahan, R. H.; Crowe Jr, J. E.
Cao, Y.; Su, B.; Guo, X.; Sun, W.; Deng, Y.; Bao, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, C.; Chai, X.; He, R.; Li, X.; Lv, Q.; Zhu, H.; Deng, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, L.; Tan, Y.; Song, L.; Wang, G.; Du, X.; Gao, N.; Liu, J.; Xiao, J.; Su, X. -D.; Du, Z.; Feng, Y.; Qin, C.; Qin, C.; Jin, R.; Xie, X. S.
Structural basis for inhibition of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir
Yin, W.; Mao, C.; Luan, X.; Shen, D. -D.; Shen, Q.; Su, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, W.; Gao, M.; Chang, S.; Xie, Y. -C.; Tian, G.; Jiang, H. -W.; Tao, S. -C.; Shen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, H.; X.u, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H. E.
Langer, L. M.; Gat, Y.; Bonneau, F.; Conti, E.
Structure of replicating SARS-CoV-2 polymerase
Hillen, H. S.; Kokic, G.; Farnung, L.; Dienemann, C.; Tegunov, D.; Cramer, P.
Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein
Walls, A. C.; Park, Y. -J.; Tortorici, M. A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A. T.; Veesler, D.
Structural basis for the recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2
Yan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q.
Structure, function and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein
Walls, A. C.; Park, Y. -J.; Tortorici, M. A.; Wall, A.; McGuire, A. T.; Veesler, D
Solving a new R2lox protein structure by microcrystal electron diffraction
Xu, H.; Lebrette, H.; Clabbers, M. T. B.; Zhao, J.; Griese, J. J.; Zou, X.; Hogbom, M.
Surpassing the physical Nyquist limit to produce super-resolution cryo-EM reconstructions
Feathers, J. R.; Spoth, K. A.; Fromme, J. C.
Xu, H. Lebrette, H.; Yang, T.; Hovmoller, S.; Hogbom, M.; Zou, X.
Nyquist 频率
剂量分割和运动校正
使用计数和超分辨率提高 DQE
| Modulation transfer function (MTF) curves | ||
|---|---|---|
| 200 kV | 300 kV | |
|
K3 |
CDS | CDS |
| Standard | Standard | |
| K2 | Standard | Standard |